Today we tested the inertia theory. The theory is that objects in motion will resist movement in a different direction. We tested this theory by having a ramp with a measuring stick next to it. Then we rolled different weighing balls down the ramp and measured how far the balls traveled.
Purpose: To test a hypothesis that a balls with more mass travel farther than balls with less mass.
Dependent Variable: Distance.
Independent Variable: Light, Medium, Heavy balls.
Standard Variables: Surface and slope.
On wood floor, 1/3 of slope:

On carpet, 1/3 of slope:
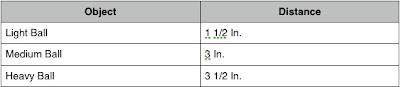
Even on the carpet, which has more friction than the wood floor, the heavier ball goes farther than the lighter ball.
Conclusion: According to these tests, the heavier balls always go farther than the lighter balls. This would support the inertia theory. However, if the floor was on a upward slope, this may not be the case.
Purpose: To test a hypothesis that a balls with more mass travel farther than balls with less mass.
Procedure:
- Set ball on ramp.
- Let go of ball.
- Measure distance ball traveled.
- Repeat procedure on each ball.
Dependent Variable: Distance.
Independent Variable: Light, Medium, Heavy balls.
Standard Variables: Surface and slope.
Data:
On wood floor, 1/3 of slope:

Heavy balls seem to go farther than light balls.
On carpet, 1/3 of slope:

Even on the carpet, which has more friction than the wood floor, the heavier ball goes farther than the lighter ball.
Conclusion: According to these tests, the heavier balls always go farther than the lighter balls. This would support the inertia theory. However, if the floor was on a upward slope, this may not be the case.



















